Dividend Value Builder Newsletter
Maximum Drawdown and the Concept of Probable Maximum Loss
Determining your probable maximum loss and choosing an equity asset allocation that is consistent with your decision will allow you to control your maximum drawdown. How much of your investment portfolio you can afford to lose is one of the most critical questions you can ask yourself.
I believe most investors have been taught to invest too aggressively. We will examine why you shouldn’t listen to the industry and media which is dominated by institutions that want you to buy and sell their products.
Portfolio Volatility and Managing Risk
Risk management analysis is an important part of any investing plan. Volatility doesn’t seem to bother most investors during bull markets. This is one of the reasons investors are “lulled” into taking on additional risk as markets rise.

Investors seeking higher rates of return gravitate toward high risk stocks. These more speculative stocks tend to lead the market up during rallies, but collapse in down markets.
The following chart exhibits the challenge of making your investment back after you lose it. Notice that the more you lose, the amount you need to break even grows exponentially.
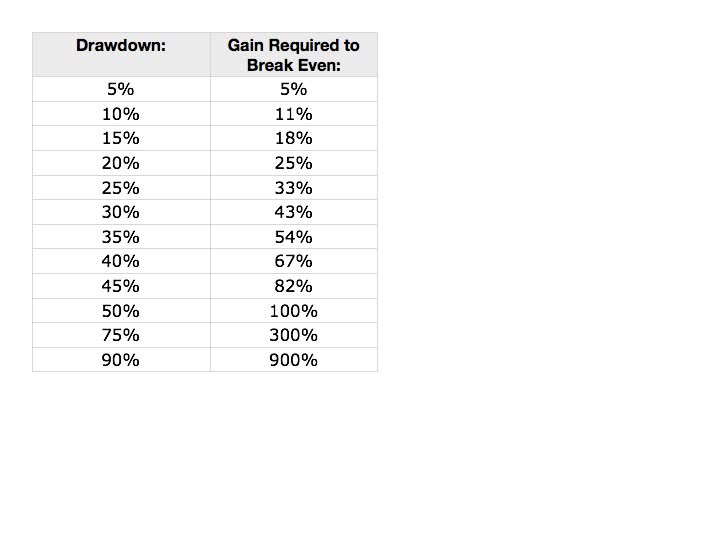
Why Is It SO Important to Avoid Investment Losses?
Portfolio volatility by itself greatly reduces your returns. This is because the money lost is capital that is no longer available for investment. If you lose only 10%, you still have 90% of your capital available for investment. If you lose 50% you only have 50% of your capital available for investment, so a 100% gain is required to get back to break even.
When you experience large losses you have less to invest and then your portfolio is in a position that can take many years to recover to break even. The reality of break even loss analysis makes losing 50% of your money intolerable! After losing 50%, IF the market gained 10% per year, and you were 100% invested, it would take 7 years (7 instead of 10 because of compounding) to get back to break even.
Maximum Drawdown
Bear markets are a part of investing. Over the last 200 years we have experienced a financial crises every 4-5 years on average. Periodically we experience bear markets that last as long as 20 years.
You must preserve the majority of your capital in bear markets to be a successful investor! This is where many investors experience failure. Over the years I’ve known people who were exuberant that they were achieving higher rates of return; only to have their portfolio destroyed in the next bear market.
Many investors invest too aggressively; they have been taught the outdated buy and hold strategy that causes them to sell in bear markets. This is because they get to the point they can’t stand the pain of a bear market anymore; often selling at the point of maximum opportunity!
What is your risk management plan? Many in the financial industry will tell you to place stops on your individual stocks. But is it possible they recommend this because it creates more trading and therefore more fees or commissions? Why should you sell a stock after it falls? If the company prospects haven’t changed maybe you should buy more instead of selling at a loss.
Probable Maximum Loss – A Better Way!
Intelligent investors will determine what their probable maximum loss limit is for a one year period. Notice this is a “probable” loss not “possible” loss. Personally, I have decided that anything over a 20% loss becomes devastating to a portfolio. You may choose a different number. But I believe this approximates an ideal or optimum number for long term growth.
Calculating Your Maximum Loss Decision
Since 1900 there have been 5 major bear markets; some of them lasting MANY years including a devastating 81% decline from Sept 1929 to June 1932.
Major Bear Markets (inflation adjusted):
1906 – 1921 = 69% decline
1929 – 1932 = 81% decline
1937 – 1949 = 54% decline
1968 – 1982 = 63% decline
2000 – 2009 = 59% decline
With the past in mind:
1. Choose an assumed probable maximum loss for equities. After reviewing the past I assume the probable maximum loss in the stock market is 40% in a year. You may choose a different number.
2. Choose the maximum loss you are willing to take to your portfolio. I have chosen 20% but you may choose a different number.
3. Divide your personal portfolio maximum loss by your assumed stock market probable maximum loss.
In my case this would calculate:
.20 divided by .40 = .50 or 50%!
The result is my target equity asset allocation is 50%. This would be the average equity target for my portfolio when market valuations are average (or fair value).
Probable Maximum Loss and Asset Allocation
When investors make asset allocation decisions they should have their maximum drawdown at the top of their list of considerations.
History shows that valuation is the key determinant of investment returns in the long run. Buying stocks when valuations are low provides greater that average rates of return with less risk. Buying stocks when valuations are high produces lower that average rates of return with greater risk.
A well planned adaptive asset allocation allows you to be more aggressive when prices are low and more conservative when bargains are unavailable. In other words, I change my equity asset allocation based on valuations. Develop an asset allocation plan that controls your investment losses.
Related Reading: 5 Risk Portfolio Management Strategies
If I can find an abundance of stocks that meet my margin of safety requirements then I might raise my equity asset allocation to 65% (or higher). If valuations are high and bargains are scarce I may lower my equity asset allocation to 25% (or lower).
Keep in mind 20% is my probable maximum loss. So I need to manage more conservatively when values are not compelling. Therefore, I have an investment loss “goal” of not losing more than 10%. If I manage with this approach, and I reach my first limit of 10%, then I still have the ability to buy low because I haven’t lost 20%.
I’ve only exceeded my investment loss goal with the AAAMP Global Value once. In 2008, with the market down 57% the AAAMP Global Value was down 12% (notice the market loss was greater than my assumed probable maximum loss of 40%). But because I had maintained my discipline I had 88% of my capital left. This allowed me to increase my equity asset allocation and buy stocks at bargain prices.
The market then rallied and the AAAMP Global Value ended the year down 2% compared to the market which finished the year down 37%. I began 2009 with 98% of my capital instead of only 63% (the amount of capital left if invested in the S&P 500).
Investors who lost 37% in 2008 did not get back to break even until 2012, and only IF they remained 100% invested in equities. It’s amazing what compounding will do to a portfolio, good and bad! Choose to be on the good side of compounding!
This is how to control investment portfolio losses: decide what your probable maximum loss is and choose an equity asset allocation that is consistent with your decision!
Additional Reading:
34 Investment Strategies and Rules To Make You A Better Investor
Minimize Large Portfolio Drawdowns
Invest With Confidence in Less Time - Manage Your Portfolio Without Behavioral Errors
